
|
National Museum of Natural History |
|
|
Ocean also wove the story of Life in the Dino Age
Part 2
| Back to Part 1 <<< |
Sea BirdPseudodontorns were large sea birds with wingspan of 18ft (5.5m) long. They are relative of Pelicans and boobies. Instead of diving into sea from sky, they were probably scooping up fish swimming at the surface of the water. The jagged jaws helped grabbing fish not to slip away. |

|
Pseudodontorn (Sea bird, life size reconstruction) 23 to 10 million years ago from Early to middle Miocene fossils are found in Maryland, Oregon and California |
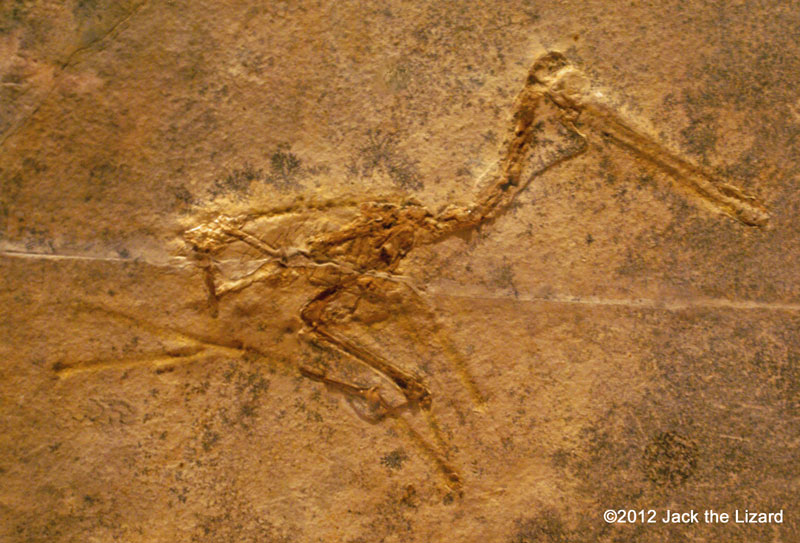
Flying ReptilePterosaurs were a group of flying reptiles that lived from the Late Triassic to the Late Cretaceous. Some of their members were so large such as Quetzalcoatlus whose wingspan was about 33ft (10m) while others were as small as swallows. All pterosaurs had wings consisted of skins and elongated fourth finger. Some of them might have fur too. Pteranodon is the one of the subfamily of pterosaurs. Like most of less primitive pterosaurs their features are short tails and toothless jaws. Pterodactylus is also the one type of pterosaurs but much smaller, whose wingspan is about 3.3ft (1m) long. They had jaws with teeth and probably ate fish. |

Pteranodon ingens (cast) 100 to 65 million years ago, Late cretaceous Kansas |

|
Pterodactylus kochi 145 million years ago Late Jurassic Germany |
Marine ReptilePlacodonts were a group of marine reptiles that back to the ocean during the Triassic period. Early placodonts had barrel like trunk, but later they developed bony plates and look like turtles. Their blunt teeth were for crushing clams and brachiopods such as rhynchonellida. The group of Placodonts includes nothosaurs. |

|
|
|
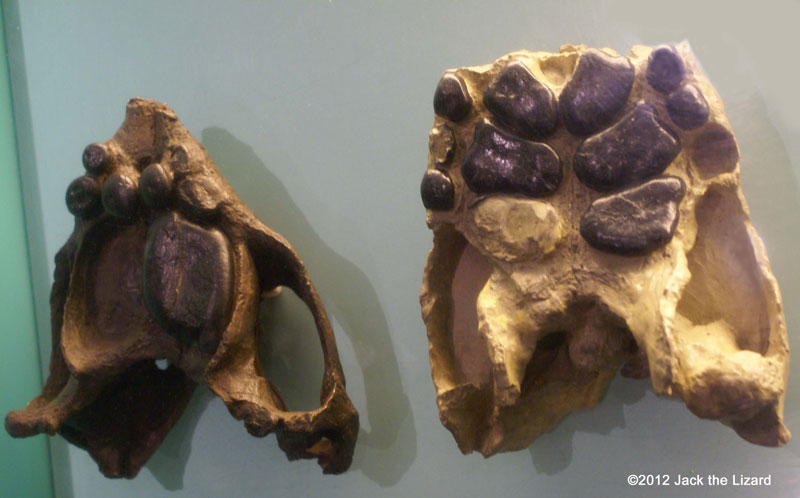
Placodont, Macroplacus raeticus (left) upper jaw (cast) 210 to 200 million years ago Late Triassic Germany |
Placodont, Placodus gigus (right) upper jaw (cast) 225 to 215 million years ago Middle Triassic Germany |
|
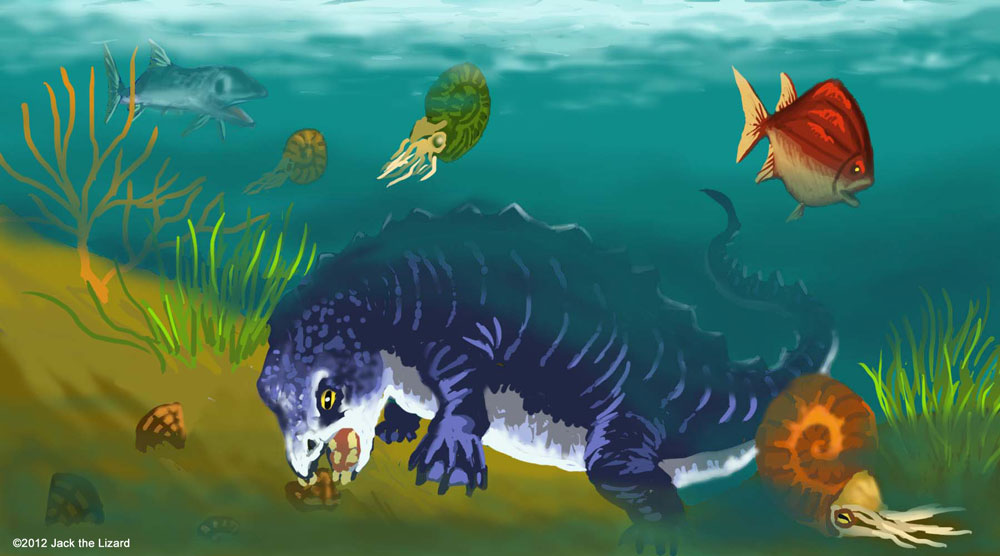

Placodont eating brachiopods in Triassic Ocean
|
Nothosaurs were a one of the Triassic marine reptiles. They had a slender body with longneck and tail, about 10ft (3m) long. Nothosaurs might have landed once in a while like seals do now. Lariosaurus was a member of nothosaurs group that lived in the shallow water. They were only 2ft (60cm) in length. Their front legs were still suited for land dwelling while the rear were evolved to shape paddle. They may be the reptiles at the transitional stage from land life to aquatic. Neuticosaurus was one of the smallest Nothosaurs that was only about 8in (16cm) in length. |
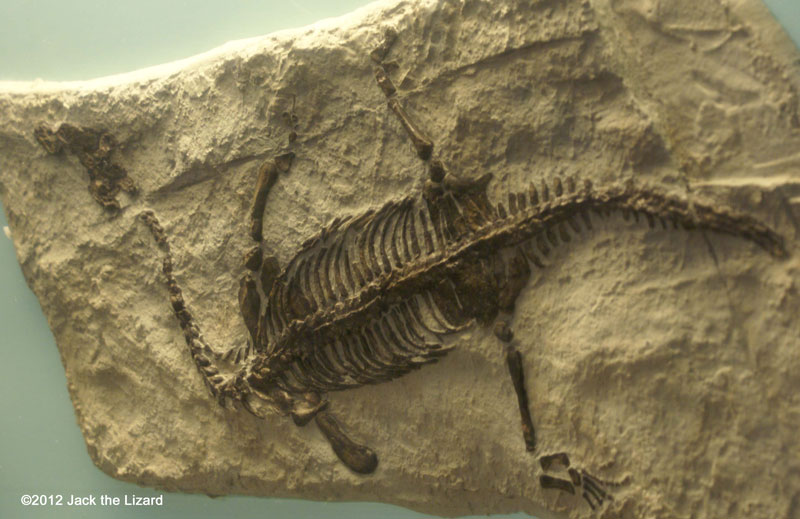

Nothosaur, Lariosaurus (cast) 225 to 215 million years ago, Middle Triassic Italy |
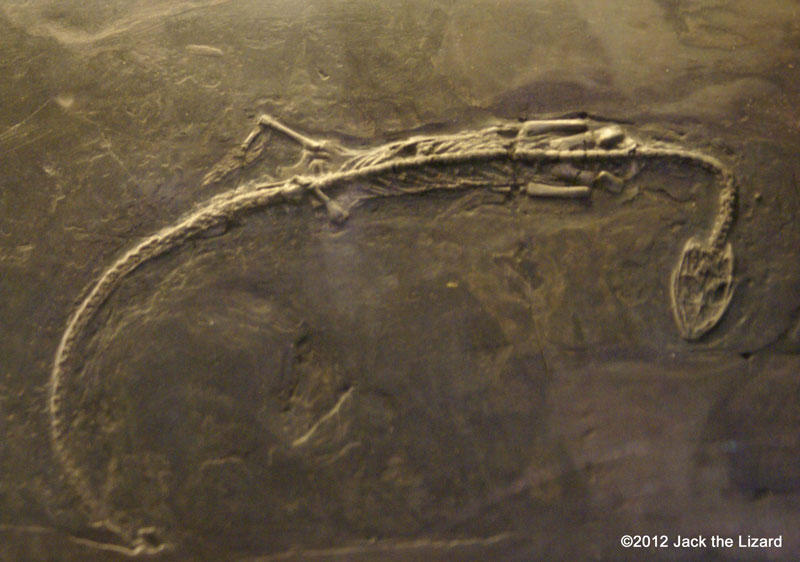

Nothosaur, Neuticosaurus 225 to 215 million years ago, Middle Triassic Switzerland |
|
Plesiosaurs adapted to the life in the sea more than their cousin nothosaurs did. Both fore and hind limbs were elongated and became paddle like flipper. The group of Plesiosaur is divided into two major groups, plesiosaurs and pliosaurs. Plesiosaurus had a small head and long neck. They swam slowly and grabbed prey passing by rather than chased them. By contrast Pliosaurs had a large head and short neck. They swam fast and hunted down fish. Dolichorhynchops grew up to 15ft (4.6m) long and ate mostly fish and squids. Few predators such as Tylosaurus and sharks had prayed upon them. One of Tylosaurus fossil had remains of juvenile Dolichorhynchops inside. Some of them see Dolichorhynchops as a type of pliosaurs, but others think Dolichorhynchops belongs to the group called “polycotylids” that are more closely related to plesiosaurus. |
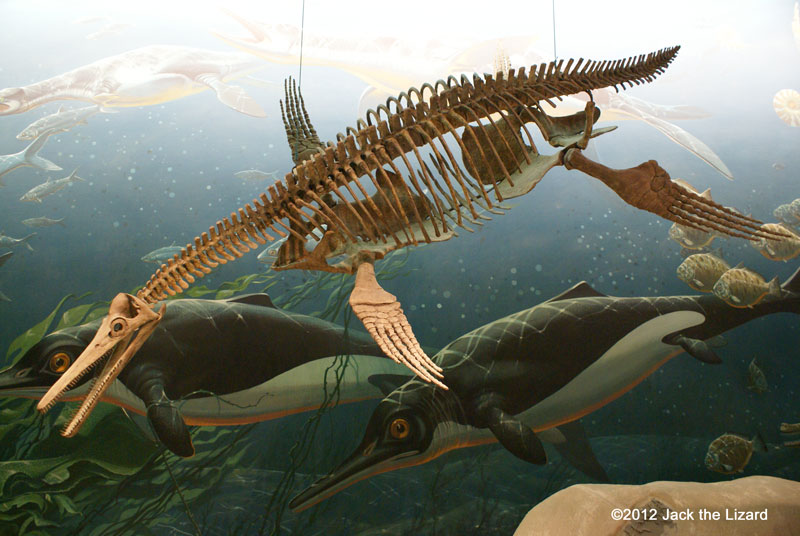

Pliosaur, Dolichorhynchops 80 to 70 million years ago, Late Cretaceous Montana |
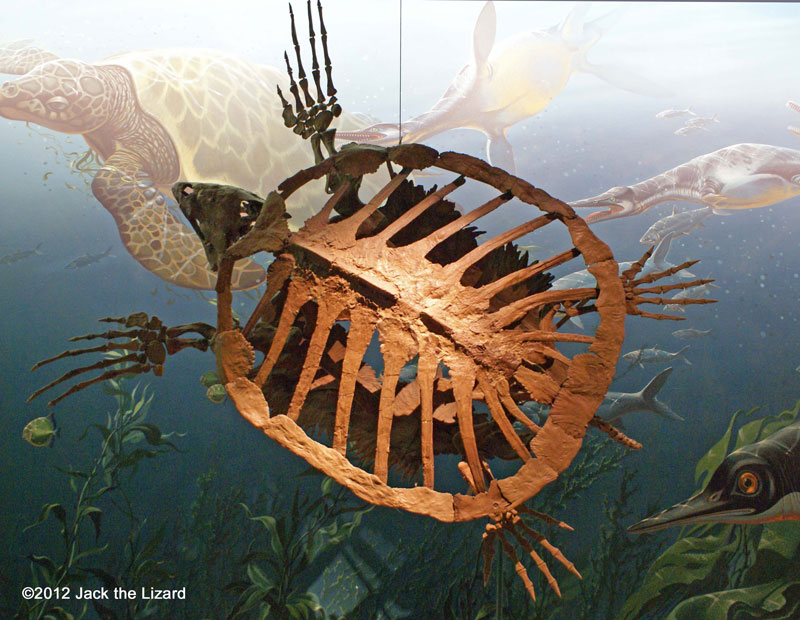

Protostega gigas 80 to 70 million years ago, Late Cretaceous Kansas |
Protostega had a leathery carapace like the one of leather back sea turtles. Because of lightly designed back bone they could swim fast with powerful front legs. Protostega grew up to 10ft (3m) long, they were one of the largest sea turtles ever lived. They preyed upon jellyfish and shellfish. |
|
Ancestor of Crocodiles emerged Late Triassic, but some of them headed back to the ocean by the beginning of the Jurassic period. They propelled themselves by undulating long powerful tail and swallowed rocks for a balance in the water. Rocks also helped their digestion in the stomach. Steneosaurus lived in shallow seas and probably caught fish with their thin sharp teeth. The features of Steneosaurus are long and narrow snout and slender body with small forelimbs. Steneosaurus probably grew up to 13ft (4m) in length. |
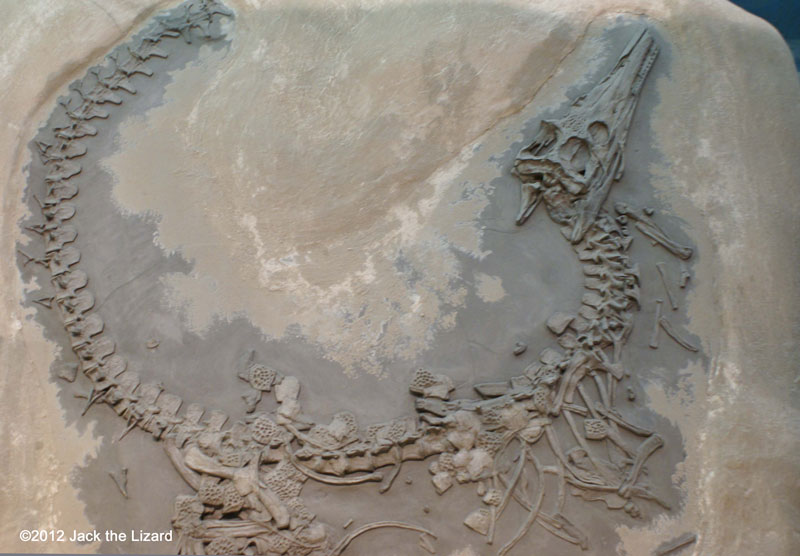

Steneosaurus 195 to 180 million years ago, Early Jurassic Germany |
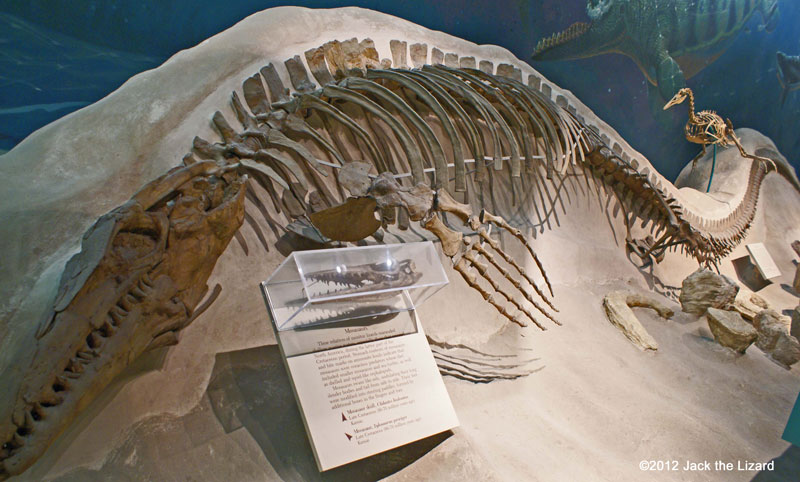

Mosasaur, Tylosaurus proriger 80 to 70 million years ago, Late Cretaceous Kansas |
Mosasaurus were related to monitor lizard, but lived in shallow water. They swam like eel, waved their body from side to side. Tylosaurus was the largest in the mosasaurus group. They probably had huge appetite, their pray includes such as ammonites, sea turtles, smaller mosasaurus and plesiosaurs. Globidens was about 20ft (6m) long and had streamed body with flippers as well as other mosasaurus did. But unlike other mosasaurus Globidens had rounded teeth for crushing shells of turtles, ammonites and clams. Clidastes was a small mosasaurus about 6.6ft (2m) long. |

Mosasaur, Globidens alabamensis 80 to 70 million years ago, Late Cretaceous Alabama |
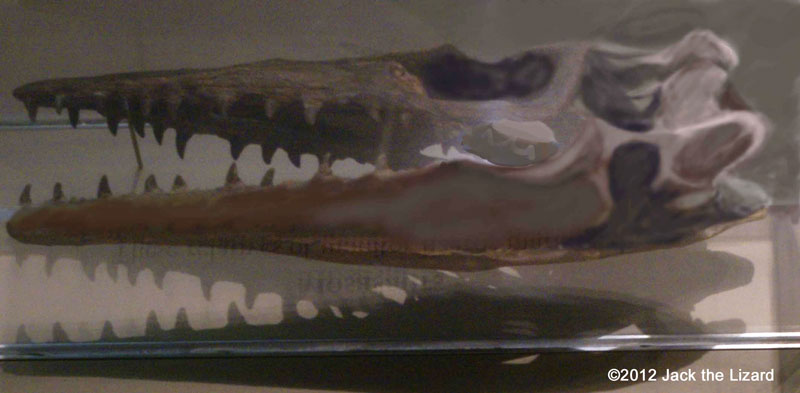
Mosasaur, Clidastes liodontus 80 to 70 million years ago, Late Cretaceous Kansas |
|
Unidentified ancestor of Ichthyosaurs appeared the Early or Middle Triassic period and returned to the sea. They look like dolphins, but they are reptile not mammal. Their appearance is the result of the convergent evolution. They accommodated their bodies to the marine environment. Ichthyosaurs were one of the fastest swimmers in the marine reptiles. They had a tuna like body and huge developed eyes to chase fish and cephalopods. Instead of laying eggs, they had borne young in the water. |

Ichthyosaur, Stenopterygius 190 to 180 million years ago, Early Jurassic Germany |
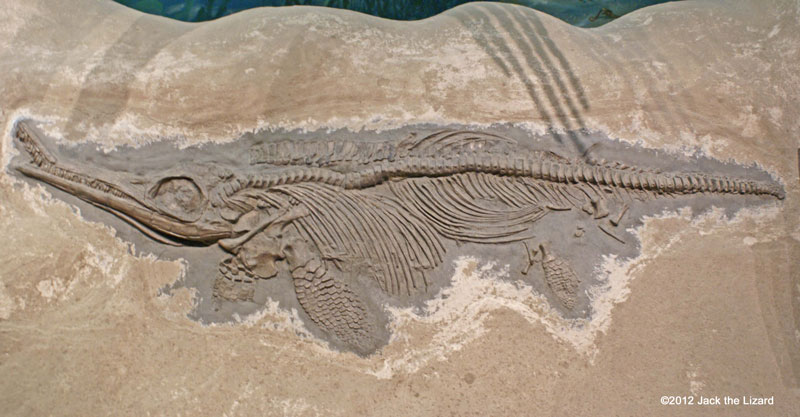

Ichthyosaur, Ichthyosaurus 195 to 180 million years ago, Early Jurassic England |
The size of Stenopterygius was about 13ft (4m) in length. Stenopterygius is similar to Ichthyosaurs, but has smaller skull and narrower mouth. Ichthyosaurs were about 6.6ft (2m) long and lived in high seas. They are most known type among the group of Ichthyosaur. Hunting depended on their large keen eyes and inner ears that sense the water vibration through the bone. |
Marine Mammal
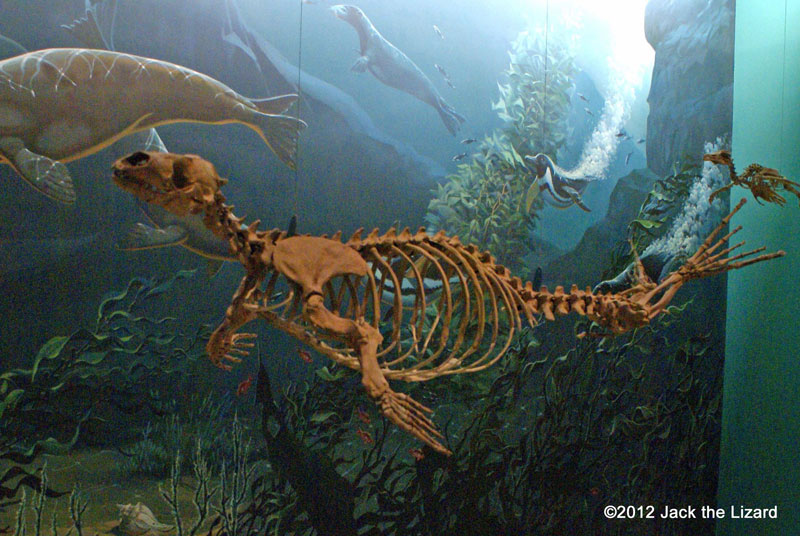

Acrophoca longirostris, early seal, Early Pliocene, Peru
Acrophoca is relative of leopard seal.
Ancient Whales
|
Whales are divided into two groups, toothed whales (Odontoceti) and baleen whales (Mysticeti). Both of them are closely related to ancestors of hippopotamus. Toothed whales such as dolphins and sperm whales have one blow whole and are relatively smaller than baleen whales. On the other hand baleen whales such as bowhead whales and blue whales have two blow holes and generally larger body than toothed whales. |

Maiacetus inuus 49 to 40 million years ago, Middle Eocene Eastern Pakistan |
Ancient toothed whalesMaiacetus was early cetacean that had feet with flippers and probably life similar to seals. They still had hind legs, but spent most of their time in the sea except giving birth on the land. Dorudon was related to Maiacetus, but its hind limbs were much smaller and entirely lived in the ocean. |
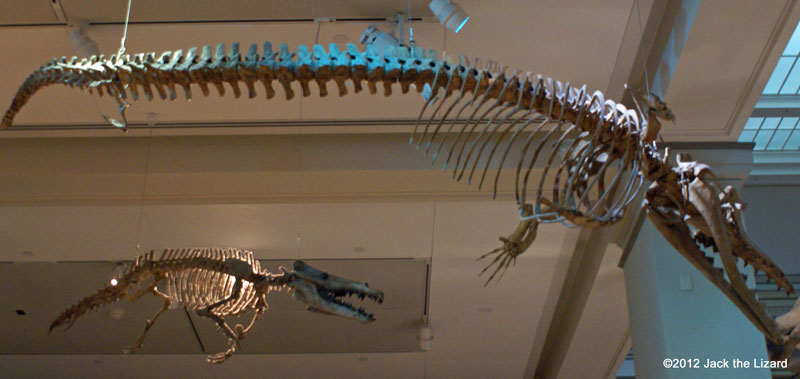
Dorudon atrox 38 to 36 million years ago, Middle Eocene Northern Egypt |

|
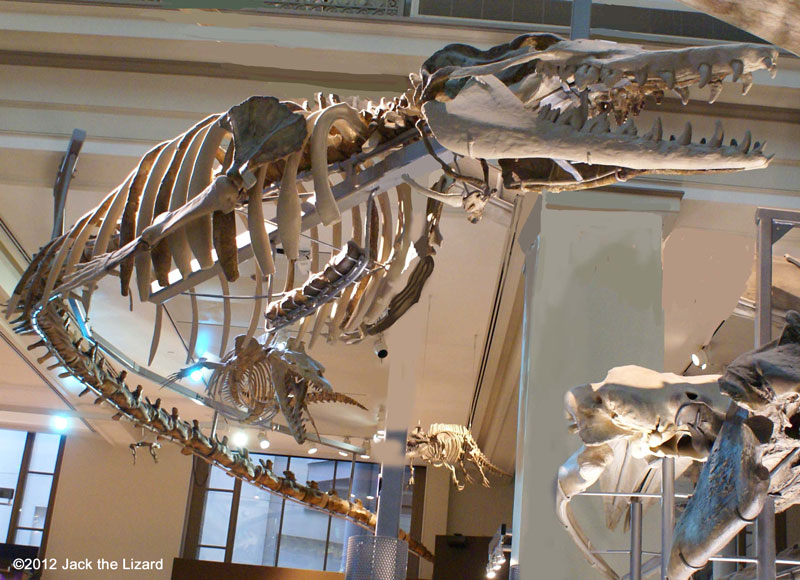
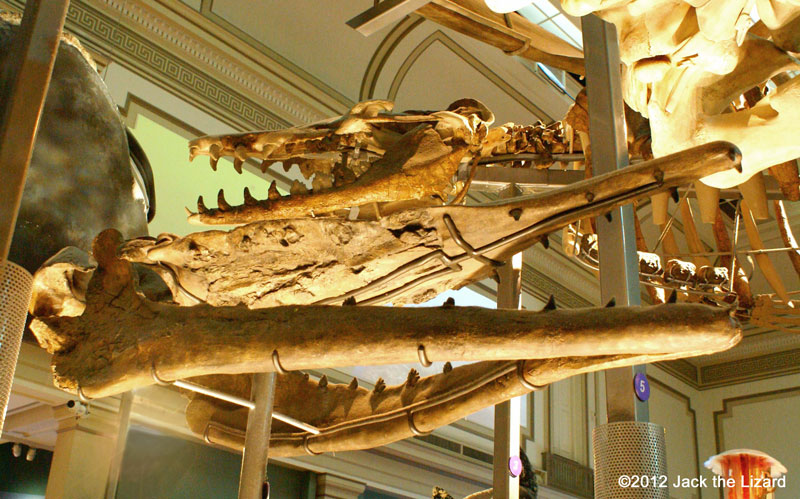
Basilosaurus swam in the same ocean that Dorudon did. The elongated body is the noticeable feature of Basilosaurus. Basilosaurus was probably fast swimmer and caught fish, sharks and molluscs. |
|
Basilosaurus cetoides 40 to 35 million years ago, Middle Eocene Mississippi and Alabama the only real specimen on display in the world |
|
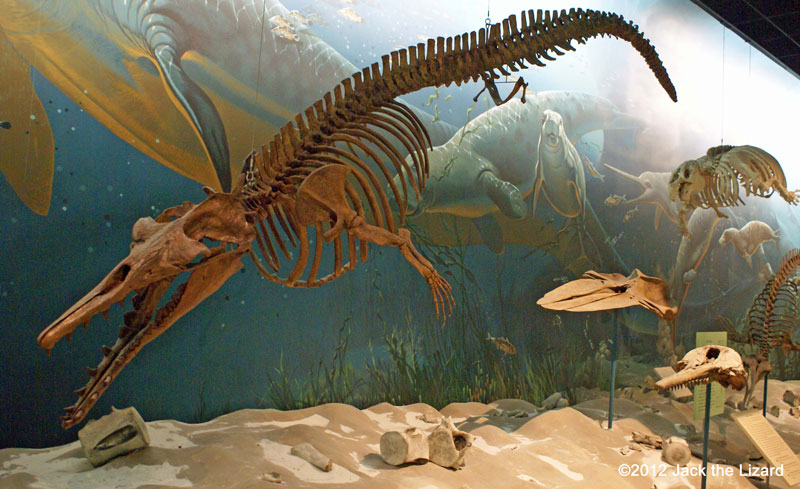
Zygorhiza is relative of Basilosaurus. |

|
|
Zygorhiza kochii early teethed whale 39 to 37 million years ago, Late Eocene Southeastern United States |

|
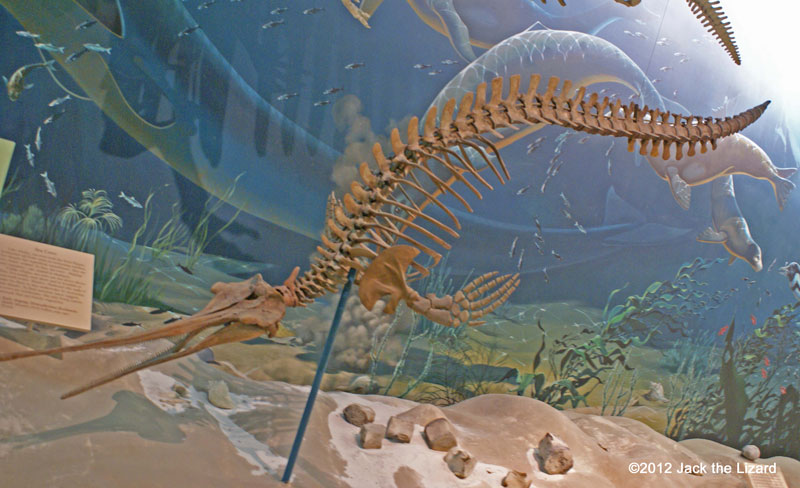
Xiphiacetus early dolphin 16 to 10 million years ago, Middle Miocene Maryland |
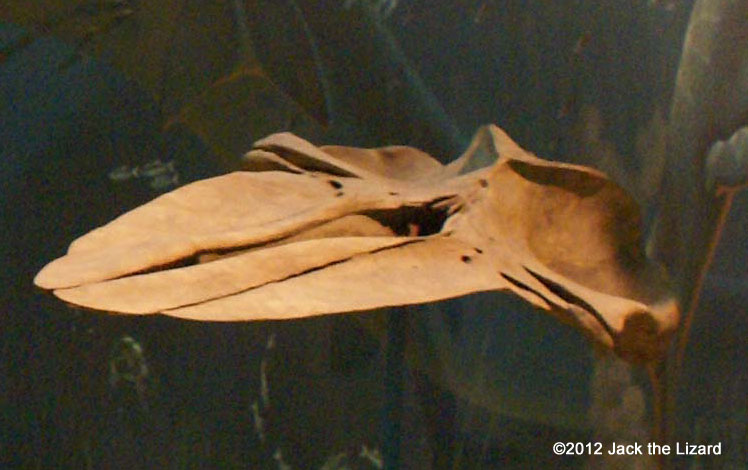
Ancient baleen whalesLlanocetus has both teeth and baleen like sieve. They were an intermediate stage in the evolution of baleen whales. |
|
|
Llanocetus denticrenatus early baleen whale 35 to 34 million years ago, Eocene Antarctica |

|
Diorocetus was baleen whale even no fossilized baleen was left, because toothless jaw bone clearly indicates that. |
|
Diorocetus hiatus baleen whale 16 to 10 million years ago, Middle Miocene Maryland |
| Back to Part 1 <<< |